ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) injuries are a common type of knee injury that can occur in athletes, especially in sports that involve sudden stops, changes in direction, and jumping. The ACL is a crucial ligament that provides stability to the knee and helps to prevent excessive forward movement of the lower leg relative to the thigh.
ACL injuries can range from mild sprains to complete tears. The latter can require surgical intervention. An ACL injury can also limit an individual’s ability to participate in physical activities, causing significant impairment and reduced quality of life.

The diagnosis of ACL injuries typically involves a physical examination and imaging studies, such as an MRI. In some cases, a diagnostic arthroscopy may be performed to confirm the extent of the injury. Treatment options for ACL injuries can vary depending on the severity of the injury, the patient’s age, and their desired level of activity.
Symptoms of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries
Symptoms of an ACL injury can include pain, swelling, instability, and difficulty bearing weight on the affected knee. More about symptoms below.
- Pain: An ACL injury can result in sudden, severe pain in the knee, especially when the injury occurs as a result of a twisting or turning movement. Pain may be accompanied by a popping or snapping sensation.
- Swelling and Stiffening: Swelling is a common symptom of an ACL injury and can occur within hours of the injury. The knee may become swollen and stiff, making it difficult to move.
- Increased Instability: An ACL injury can result in instability in the knee, making it difficult to walk or stand. The knee may feel like it is giving way or buckling.
- Decreased Range of Motion: An ACL injury can cause the knee to become stiff, making it difficult to bend or extend the leg fully.
- Difficulty Bearing Weight: An ACL injury can make it difficult to bear weight on the affected leg, especially in the days following the injury.
- Loss of Confidence: An ACL injury can result in a loss of confidence in the affected knee, making it difficult to participate in physical activities.
It is important to seek prompt medical attention if you suspect that you have suffered an ACL injury. An accurate diagnosis can be made through a physical examination and imaging studies, such as an MRI. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to reduce the risk of long-term complications and improve the outcome of the injury.
To summarise, ACL injuries are a common type of knee injury that can result in significant pain and disability. By understanding the symptoms of an ACL injury, individuals can seek prompt medical attention and receive the appropriate treatment. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to reduce the risk of long-term complications and improve the outcome of the injury.
Treatments for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries
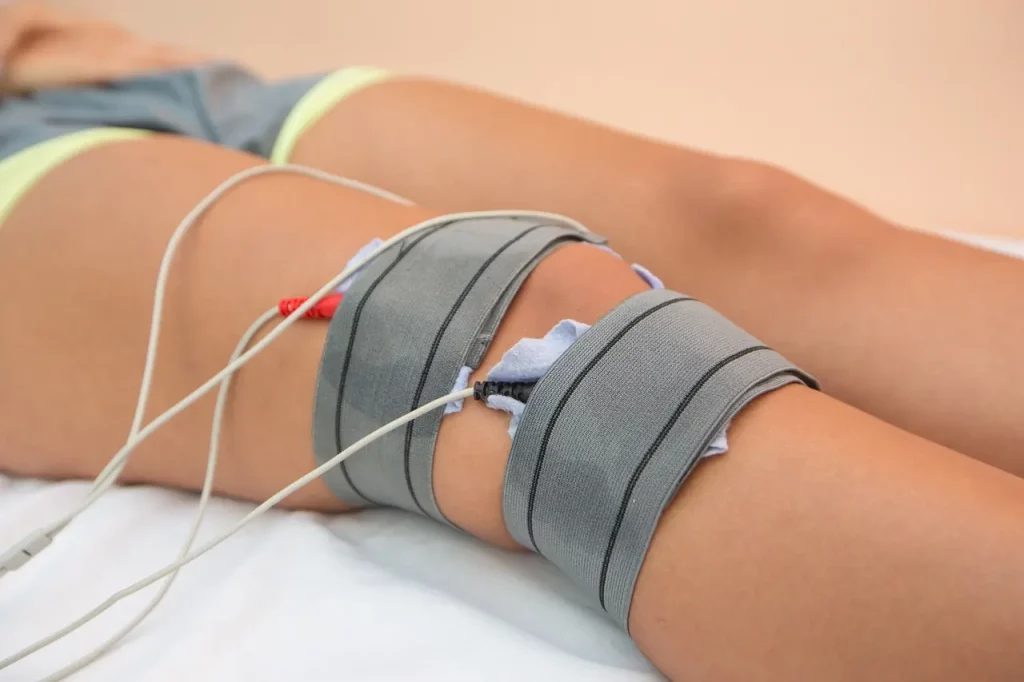
Now that we have discussed the symptoms of ACL injuries, let’s move on to discussing the various treatments for an ACL injury.
Non-Surgical Treatments
For minor ACL injuries, non-surgical treatments, such as rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), physical therapy, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may be recommended. Physical therapy can help to improve knee strength and flexibility and reduce pain.
Knee Braces
In some cases, a knee brace can be used to support the knee and reduce the risk of further injury. Knee braces can help to improve stability and reduce pain.
Surgical Treatments
For more severe ACL injuries, surgical treatment may be recommended. The most common surgical procedure for an ACL injury is ACL reconstruction, which involves replacing the damaged ligament with a tissue graft. The tissue graft can come from the patient’s own body, such as the patellar tendon or the hamstring tendon, or from a donated tissue.
Rehabilitation
Following ACL surgery, rehabilitation is essential to regain knee strength and stability. Physical therapy can help to improve flexibility and strength and reduce pain. A rehabilitation program may involve exercises to improve knee range of motion, strength, and stability, as well as balance and coordination.
Return to Activity
The timeline for returning to physical activity following ACL surgery will vary depending on the individual’s age, the type of physical activity, and the severity of the injury. In general, individuals can return to low-impact activities, such as cycling and swimming, within three to six months of surgery. Return to high-impact activities, such as running and jumping, may take up to one year or longer.
Treatment for an ACL injury will depend on the severity of the injury and the individual’s age and physical activity level. Non-surgical treatments, such as rest, ice, and physical therapy, can be effective for minor ACL injuries. For more severe ACL injuries, surgical treatment, such as ACL reconstruction, may be recommended. Rehabilitation is essential following ACL surgery to regain knee strength and stability, and to reduce pain and improve the outcome of the injury.
How to Avoid ACL Injuries

ACL injuries can be devastating for athletes and active individuals. Fortunately, there are steps that can reduce the risk and maintain knee stability. Let’s discuss some practical strategies for avoiding ACL injuries.
- Strengthen Muscles Surrounding the Knee: Strong quadriceps and hamstrings can help to stabilise the knee and reduce the risk of ACL injury. Squats, lunges, and leg presses are exercises that can help to build strength in these muscle groups.
- Improve Flexibility: Tight muscles can increase the risk of injury, so it is important to regularly stretch the muscles surrounding the knee. Dynamic stretching, such as leg swings and high knees, can help to improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injury.
- Improve Balance: Maintaining good balance can help to prevent falls and reduce the risk of ACL injury. Exercises such as single-leg squats, balance boards, and wobble cushions can help to improve balance and stability.
- Wear Proper Equipment: Wearing proper shoes with good support and cushioning can help to reduce the risk of knee injuries. Wearing knee braces and other protective gear can also help to prevent knee injuries.
- Warm-Up Pre-Physical Activity: A proper warm-up can help to prepare the body for physical activity and reduce the risk of injury. Light aerobic activity, such as jogging, and dynamic stretching can help to increase blood flow and loosen the muscles.
- Avoid Overtraining: Overloading the knee by doing too much too soon can increase the risk of injury. Gradually increasing the intensity and duration of physical activity can help to prevent knee injuries.
- Avoid High-Risk Activities: Certain activities, such as downhill skiing, can increase the risk of ACL injury. Avoiding high-risk activities or taking the necessary precautions, such as wearing protective gear, can help to reduce the risk of injury.
As you can see, there are several strategies that people can employ to reduce the risk of ACL injuries. By following these guidelines and engaging in regular physical activity, individuals can maintain healthy knees and avoid debilitating knee injuries. Regular exercise, stretching, and proper equipment can help to prevent ACL injuries and ensure a long and active life.
Rehabilitation of ACL Injuries
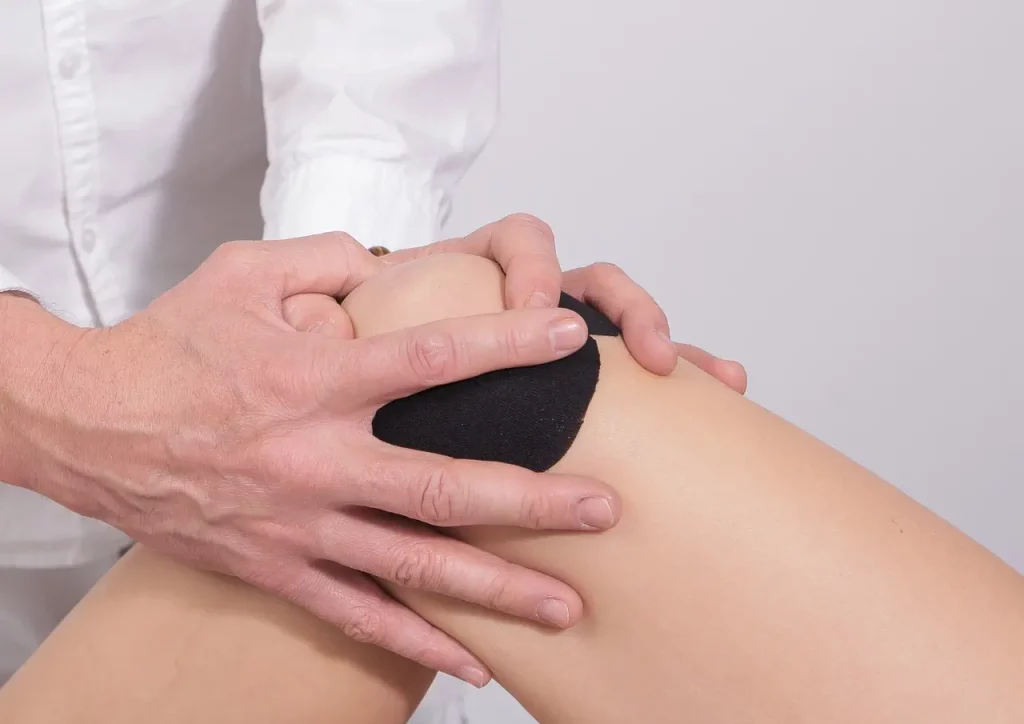
Rehabilitation following ACL surgery is crucial to ensure a successful outcome. Physical therapy can help to restore range of motion, strength, and stability to the affected knee. Additionally, it can help to prevent future knee injuries and improve overall function. A comprehensive rehabilitation program, along with proper conditioning and injury prevention strategies, can help to reduce the risk of recurrent ACL injuries.
Wrapping ACL Injuries Up
In conclusion, ACL injuries are a common and debilitating knee injury that can occur in athletes and active individuals. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help to reduce the risk of long-term complications and improve the outcome of the injury. With proper rehabilitation and injury prevention strategies, individuals can regain their prior level of function and continue to participate in physical activities.
If your looking for more posts all about the wonder of the human body and why it needs to be looked after properly, head over to this page.
Read More
- ACL Injuries and Everything You Need to Know
- 5 Types of food That Will Boost Immunity
- How to Improve Your Life with a Great Morning Routine
- The Benefits of Concentrating on Personal Development
- 6 Ways to Give Up Smoking Once and For All
Disclaimer: The information provided on Healthy Lifestyles for All is intended for general educational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. Please consult with your GP or other health professional before making any significant changes to your diet, exercise routine, or any other aspect of your lifestyle. We are not responsible for any adverse effects or consequences resulting from the use of the information provided on our blog.
Comments: I hope you enjoyed reading this post as much as I enjoyed writing it. If you liked it, please leave a comment. If you didn’t like it, disagree with something I have written (I’m okay with that), or think I got something wrong (that’s okay too), please leave a comment as well. We only truly learn from our mistakes, so I am happy to have mine pointed out.
Affiliate Links: Please also note that I may make a small amount of money if you buy one of the products I recommend in any of my blog posts. Rest assured that I have done my own due diligence, and only recommend products that have been tried and tested, and have extremely good feedback. Additionally, many of the products I recommend have 30 or 60-day money-back guarantees, so you can buy in the confidence that if a particular product is not right for you, you can get a refund.

