Arthritis is a term used to describe a group of over 100 different medical conditions that affect the joints and surrounding tissues. The main symptoms of arthritis include pain, stiffness, and swelling, which can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. There are several different types of arthritis, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and gout, to name but a few. However, in this post, we’re going to concentrate on just those four. Let’s start with osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis
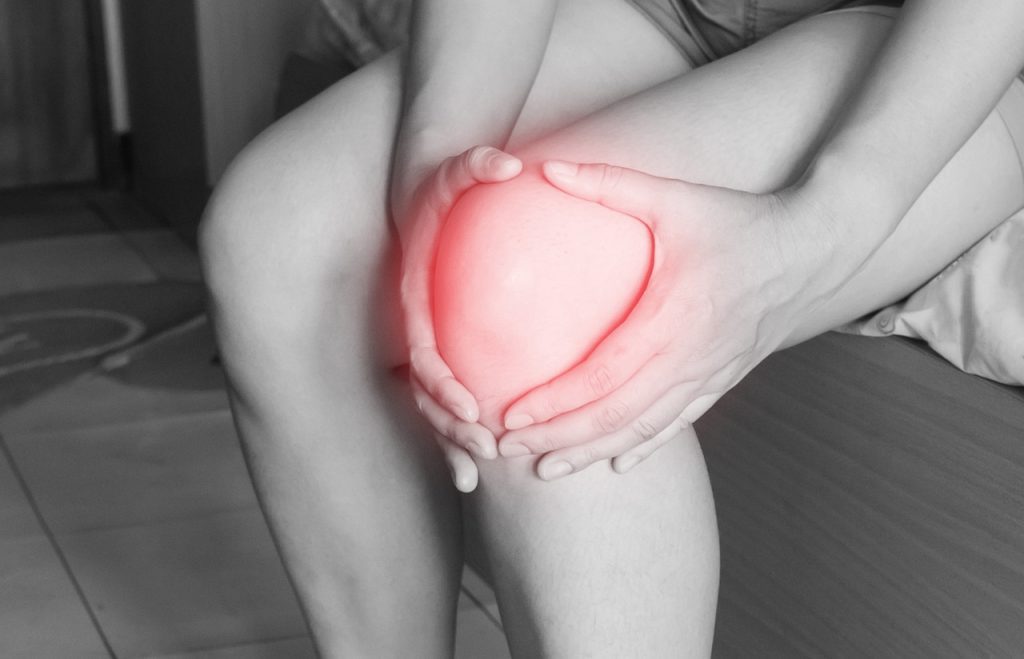
Osteoarthritis is a common and debilitating joint disorder that affects millions of people around the world. It is characterised by the gradual breakdown of the cartilage that cushions the joints. This leads to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Osteoarthritis can affect any joint in the body, but the most commonly affected joints are the hips, knees, hands, and spine.
No-one really understands the exact cause of osteoarthritis. However, many experts believe it to be a combination of factors including ageing, injury, obesity, and genetics. As people age, their cartilage gradually wears down and becomes less effective at protecting the joints. This leads to increased friction and stress on the joints, which can cause pain and inflammation. In addition, injury to a joint can weaken the cartilage and increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis.
Obesity can also increase the risk of osteoarthritis by putting extra stress on the joints. In particular, carrying excess weight around the hips and knees can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis in these areas. Genetics may also play a role in the development of osteoarthritis. It seems that some people may be more predisposed to the condition due to their genetic makeup.
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
The symptoms of osteoarthritis can vary, but typically include pain and stiffness in the affected joint. As the condition progresses, the joint may become swollen and the range of motion may be limited. In severe cases, the joint may become deformed and the patient may experience difficulty walking or performing daily activities.
Diagnosis of osteoarthritis usually involves a physical examination and a review of the patient’s medical history. X-rays or other imaging studies may also help confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of the damage to the joint.
Treatment of osteoarthritis typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical therapies. Weight loss, exercise, and physical therapy can help reduce the stress on the affected joint and improve mobility. Additionally, over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may manage pain and inflammation.
In more severe cases, stronger prescription pain medications or corticosteroid injections may be necessary. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace the affected joint. However, surgery is typically a last resort and is only considered after other treatments have failed to provide adequate relief.
Summary
To summarise, osteoarthritis is a common and debilitating joint disorder that affects millions of people around the world. The exact cause is not well understood. However factors such as ageing, injury, obesity, and genetics can increase the risk of developing the condition. Treatment typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical therapies, and in severe cases, surgery may be necessary. By taking steps to manage their osteoarthritis, patients can improve their quality of life . This, in turn, reduces the impact of this condition on their daily activities.
Rheumatoid Arthritis

Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation and damage to the joints. It is a debilitating condition that affects millions of people around the world. Also, it can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. Unlike osteoarthritis, which is a degenerative condition caused by wear and tear on the joints, RA is caused by an overactive immune system attacking the joints.
RA typically affects the smaller joints in the hands and feet. However, it can also affect the larger joints such as the hips, knees, and shoulders. The inflammation caused by RA can lead to pain, stiffness, and swelling in the affected joints. Over time, this can cause the joint to become deformed and lead to a loss of function.
As usual, people don’t understand the exact cause of RA. However, researchers believe it to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some people may be more predisposed to the condition due to their genetic makeup. Additionally, certain environmental factors such as exposure to tobacco smoke or other environmental toxins may increase the risk of developing RA.
Diagnosis of RA usually involves a physical examination, a review of the patient’s medical history, and laboratory tests such as blood tests and X-rays. The results of these tests can help confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of the inflammation and damage to the joints.
Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Treatment of RA typically involves a combination of medical therapies and lifestyle changes. Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) can help reduce inflammation and slow the progression of the disease. In addition, physical therapy and exercise can help improve joint function. These reduce the impact of RA on a person’s daily activities.
In severe cases, biologic drugs such as tumour necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors may assist managing RA. These drugs target specific parts of the immune system to reduce inflammation and slow the progression of the disease. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace damaged joints.
It is important for people with RA to work closely with their healthcare provider. Together, they need to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that meets their individual needs and goals. In addition, making lifestyle changes definitely help. These include maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular physical activity can help manage symptoms and improve overall health.
Summary
In summary, rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation and damage to the joints. The exact cause is not well understood, However, a combination of genetic and environmental factors may increase the risk of developing the condition. Treatment typically involves a combination of medical therapies and lifestyle changes. In severe cases, biologic drugs or surgery may be necessary. By working closely with their healthcare provider, people with RA can manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Psoriatic Arthritis
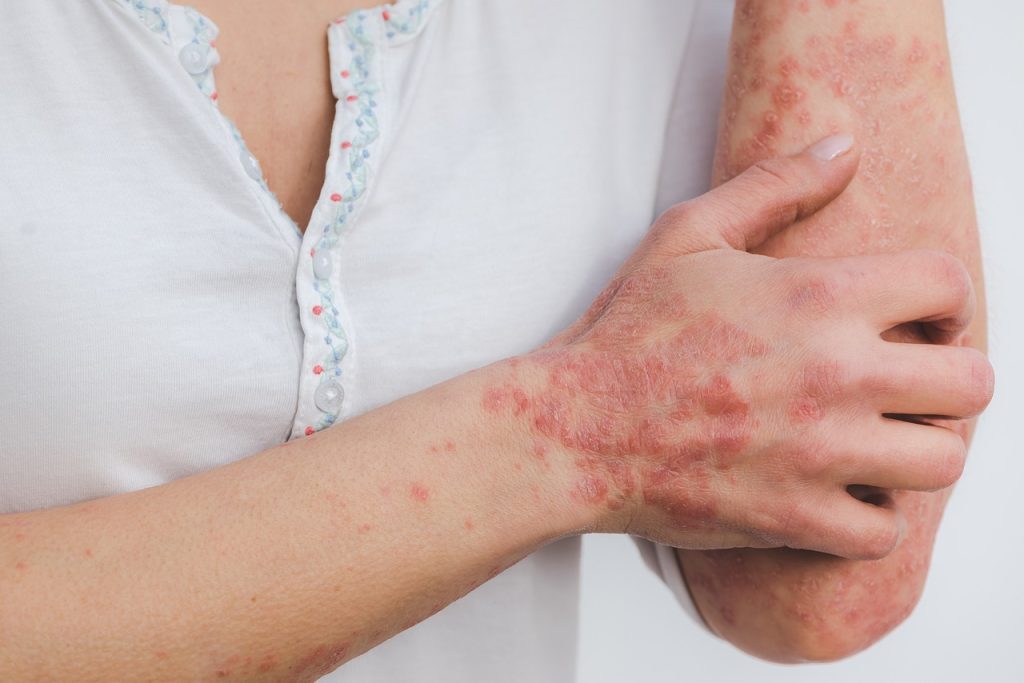
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a type of inflammatory arthritis that affects people with psoriasis. Psoriasis is a a chronic skin condition characterised by patches of red, scaly skin. While psoriasis and PsA are distinct conditions, they often occur together. Up to 30% of people with psoriasis developing PsA at some point in their lives.
PsA affects the joints, causing inflammation and pain, as well as swelling and stiffness. PsA is similar to RA, in that it is an autoimmune disorder that causes the body’s immune system to attack the joints. And, of course, like most other types of arthritis, no one knows the exact cause of PsA. Having said that, experts believe genetic and environmental factors play a role.
Symptoms of PsA can vary widely, with some people experiencing only mild symptoms, while others may experience severe joint pain and disability. Common symptoms of PsA include joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, especially in the fingers, toes, knees, and spine. In addition, people with PsA may experience fatigue, reduced range of motion, and difficulties with daily activities such as dressing, cooking, and bathing.
Diagnosis of PsA typically involves a physical examination, a review of the patient’s medical history, and laboratory tests such as blood tests and X-rays. The results of these tests can help confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of the inflammation and damage to the joints.
Treatment of Psoriatic Arthritis
Treatment of PsA typically involves a combination of medical therapies and lifestyle changes. Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) can help reduce inflammation and slow the progression of the disease. In addition, physical therapy and exercise can help improve joint function and reduce the impact of PsA on a person’s daily activities.
In severe cases, biologic drugs such as tumour necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors may be used to manage PsA. These drugs target specific parts of the immune system to reduce inflammation and slow the progression of the disease. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace damaged joints.
It is important for people with PsA to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that meets their individual needs and goals. In addition, making lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular physical activity can help manage symptoms and improve overall health.
Summary
Summarising, psoriatic arthritis is a type of inflammatory arthritis that affects people with psoriasis. It is caused by an overactive immune system attacking the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and joint damage. Treatment typically involves a combination of medical therapies and lifestyle changes, and in severe cases, biologic drugs or surgery may be necessary. By working closely with their healthcare provider, people with PsA can manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Gout
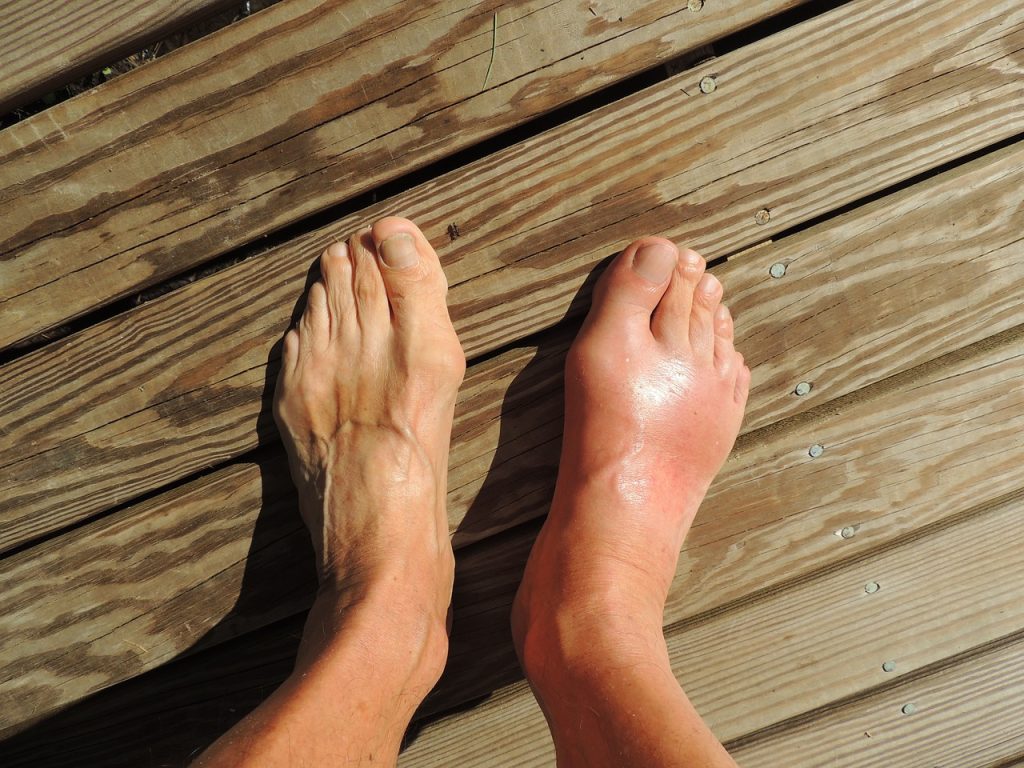
Gout is a type of arthritis that is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. This buildup can lead to sudden and severe attacks of pain, redness, and swelling in the affected joint, often in the big toe. Gout is a common form of arthritis which can affect people of any age, although men over the age of 40 are the most susceptible.
Gout occurs when the body produces too much uric acid or does not properly eliminate it from the bloodstream. The excess uric acid crystallises and deposits in the joints, causing inflammation and pain. Gout most commonly affects the big toe joint, but it can also affect the knees, ankles, wrists, fingers, and elbows.
The symptoms of gout can come on suddenly and can be very severe. In addition to joint pain and swelling, people with gout may also experience redness and warmth in the affected joint, as well as limited joint movement. The attacks of gout can last for several days to a week, and without proper treatment, they can occur more frequently over time.
There are several factors that can increase the risk of developing gout, including genetics, a diet high in purines (substances found in foods such as red meat, organ meats, and seafood), and certain medical conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and kidney disease. Certain medications, such as diuretics, can also increase the risk of developing gout.
Diagnosing Gout
Diagnosing gout can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to other forms of arthritis. A doctor will typically perform a physical examination and take a medical history, and may also perform a blood test to measure the levels of uric acid in the bloodstream. In some cases, a doctor may also remove fluid from the affected joint and examine it under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis of gout.
Treatment for gout typically involves reducing the inflammation and pain, and preventing future attacks. This can be done through a combination of medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, and corticosteroids, as well as lifestyle changes such as losing weight, reducing alcohol consumption, and eating a healthy diet low in purines. In severe cases, a doctor may also recommend a uric acid-lowering medication, such as allopurinol, to help prevent future attacks of gout.
Summary
To summarise, gout is a type of arthritis that is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. It can cause sudden and severe attacks of pain and swelling in the affected joint. Diagnosis is through a physical examination, medical history, and blood test. Treatment for gout typically involves reducing the inflammation and pain. Additionally, preventing future attacks through a combination of medications and lifestyle changes helps. If you are experiencing symptoms of gout, it is important to see a doctor for a proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Wrapping Up This Post on Artritis
In conclusion, there are several different types of arthritis, each with its own specific set of symptoms, causes, and treatments. Understanding the different types of arthritis is important in order to receive an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment. If you are experiencing symptoms of arthritis, it is important to see a doctor for a proper evaluation and diagnosis.
If your body is causing you grief, then head over here where you can read lots of posts about why your body may be playing up, what to do about it, and how to start living the life you used to. Looking for specific help for arthritis? Then head over to this UK website where you can find lots of advice and products related to arthritis.
Read More
- Testolan Supplement – Male Testosterone Management
- The Role of Genetics in Obesity: Myths and Realities
- How Maintaining a Healthy Mindset Improves Your Life
- 3 Surprising Sources of Protein, Fibre, and Essential Vitamins
- Nutritional Needs of Teenagers: A Comprehensive Guide
Disclaimer: The information provided on Healthy Lifestyles for All is intended for general educational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. Please consult with your GP or other health professional before making any significant changes to your diet, exercise routine, or any other aspect of your lifestyle. We are not responsible for any adverse effects or consequences resulting from the use of the information provided on our blog.
Comments: I hope you enjoyed reading this post as much as I enjoyed writing it. If you liked it, please leave a comment. If you didn’t like it, disagree with something I have written (I’m okay with that), or think I got something wrong (that’s okay too), please leave a comment as well. We only truly learn from our mistakes, so I am happy to have mine pointed out.
Affiliate Links: Please also note that I may make a small amount of money if you buy one of the products I recommend in any of my blog posts. Rest assured that I have done my own due diligence, and only recommend products that have been tried and tested, and have extremely good feedback. Additionally, many of the products I recommend have 30 or 60-day money-back guarantees, so you can buy in the confidence that if a particular product is not right for you, you can get a refund.

